When searching for wine fermentation tanks for sale, buyers notice wide price ranges influenced by tank size, material, and features. Stainless steel tanks, for example, can cost anywhere from $1,000 to over $30,000, depending on capacity and included technology.
| Material Type | Capacity Range | Average Price Range (2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel Tanks | 100L – 50,000L+ | $1,000 – $30,000+ |
| Oak Barrels | 225L – 600L | $300 – $1,200 per barrel |
| Concrete Tanks | 600L – 2,000L+ | $2,000 – $10,000+ |
| Plastic Tanks (HDPE) | 20L – 1,000L | $50 – $500 |
Features like temperature control, automation, and high-grade stainless steel increase both quality and price. Selecting the right wine fermentation tanks for sale requires careful attention to these details for a smart investment.
Key Takeaways
- Prices of wine fermentation tanks vary mainly due to tank size, material quality, and included features like temperature control and automation.
- Stainless steel tanks, especially grades 304 and 316, offer durability and better wine quality but come at a higher initial cost with long-term value.
- Tank design types such as open, closed, conical, and flat-bottom affect both functionality and price, so choose based on your winemaking needs.
- Features and accessories like cooling jackets, clean-in-place systems, and automation improve efficiency but increase the tank’s price.
- Research seller reputation, request detailed quotes, and verify certifications to ensure you invest in a reliable tank that fits your budget and production goals.
Why Prices of Wine Fermentation Tanks for Sale Vary
Tank Size and Capacity Differences
Tank size stands as one of the most visible factors influencing price. Larger tanks require more raw materials and stronger construction, which increases manufacturing costs. For example, a 250-gallon tank may cost around $3,350, while a 1,000-gallon tank can reach $6,200 or more. The price continues to rise with capacity, especially for commercial operations.
| Tank Size (Gallons) | Approximate Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| 5 | $150 – $300 |
| 50 | $1,000 – $2,500 |
| 250 | $3,350 |
| 500 | $4,300 – $10,000 |
| 1,000+ | $6,200 – $10,000+ |
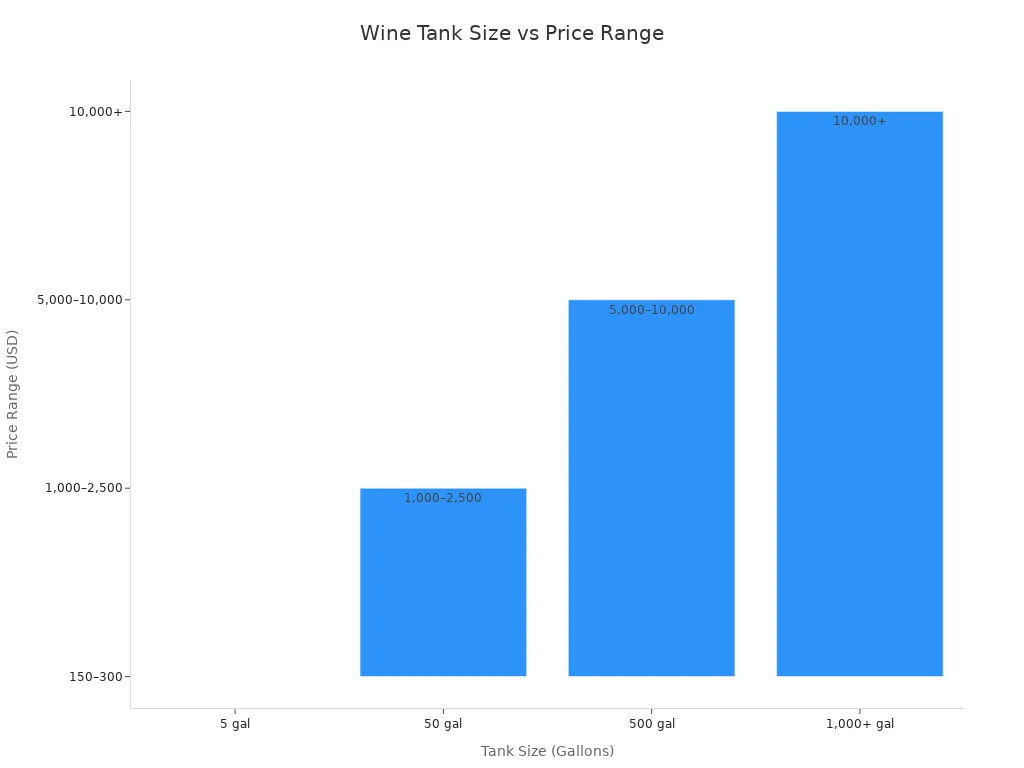
Capacity does not act alone. Material quality, tank design, and special features also play major roles. For instance, a large tank with advanced temperature control will cost more than a basic tank of the same size. Stainless steel wine fermentation tanks, especially those with variable-capacity tanks, offer flexibility for both small and large producers, but their price reflects this adaptability.
Stainless Steel Grades and Material Quality
Material quality directly impacts both price and performance. Stainless steel wine fermentation tanks dominate the market due to their durability, ease of cleaning, and ability to maintain wine flavor neutrality. Two grades appear most often: 304 and 316 stainless steel.
- Grade 304 stainless steel offers a balance between cost and corrosion resistance. Most wineries choose this grade for its reliability and value.
- Grade 316 stainless steel provides enhanced corrosion resistance, making it suitable for more demanding environments. This grade increases the initial investment but extends the tank’s lifespan and reduces maintenance needs.
Choosing between these grades affects both the upfront cost and long-term value. Tanks with thicker walls or higher-grade steel command higher prices but deliver greater durability and lower risk of contamination. Stainless steel wine fermentation tanks remain a long-term investment for wineries seeking consistent quality.
Design Types: Open, Closed, Conical, and Flat-Bottom
Tank design shapes both functionality and price. Open-top fermentation tanks allow oxygen exposure, which can benefit certain wine styles. These tanks feature a basic design and usually cost less. Open-top fermentation tanks suit small batches and traditional winemaking methods.
Closed fermentation tanks provide a sealed environment, preventing contamination and allowing for precise temperature control. These tanks often include advanced features, such as cooling jackets, which increase their price. Closed fermentation tanks are ideal for wineries prioritizing hygiene and consistency.
Conical tanks, also known as truncated cone fermenters, feature a cone-shaped bottom that simplifies sediment removal. This design adds complexity and cost but improves efficiency during racking and cleaning. Flat-bottom tanks offer a simpler, more affordable option, making them popular for straightforward fermentations.
| Tank Type | Design Feature | Cost Implication and Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Conical Tanks | Cone-shaped bottom for sediment removal | More complex design, higher cost, efficient for racking |
| Flat-Bottom Tanks | Simple flat bottom | Less expensive, easy to clean, suitable for simple fermentations |
| Open Fermenters | Open top, oxygen exposure | Basic design, lower cost, traditional winemaking |
| Closed Fermenters | Sealed lid, contamination prevention | More complex, higher cost, supports temperature control |
Variable-capacity tanks, which allow winemakers to adjust the internal volume, add further flexibility and can influence price based on their sealing mechanisms and included features.
Tip: When comparing wine fermentation tanks for sale, buyers should consider not only the initial price but also how tank design and material quality affect long-term value and winemaking flexibility.
Features and Accessories Included
Features and accessories play a major role in the final price of a wine fermentation tank. Buyers often see a wide range of options, each adding value and functionality. Some features improve the winemaking process, while others focus on convenience and safety.
- Advanced temperature control systems, such as cooling jackets and built-in sensors, help winemakers maintain precise fermentation conditions. These systems increase the cost but offer better control over the final product.
- Automation and remote monitoring capabilities allow operators to track and adjust fermentation from a distance. This technology boosts efficiency and raises the price.
- Conical bottoms make sediment removal easier. Tanks with this design cost more but save time during cleaning and racking.
- Clean-in-place (CIP) systems simplify cleaning and improve hygiene. These systems add to the initial investment but reduce labor and downtime.
- Airtight lids and insulation help maintain stable fermentation environments. These features protect the wine and increase the tank’s price.
- Mobility options, such as tank stands and leveling feet, make moving and positioning tanks easier. These accessories add to the overall cost.
- Accessories like sample valves, manways for cleaning access, tri clamp connectors, sight glasses, and pump-over systems enhance usability. Each addition increases the tank’s price but provides greater flexibility.
- High-grade stainless steel materials, such as 304 or 316L, offer durability and hygiene benefits. Tanks made from these materials command higher prices.
- Certifications for safety and hygiene compliance ensure quality and regulatory adherence. These certifications increase the cost but provide peace of mind.
- Customization options, including unique tank shapes, multi-zone heating or cooling, IoT sensor integration, and personalized branding, further elevate the price.
Bundled features and accessories often provide better value than purchasing items separately. Many suppliers include essential accessories, such as thermometers, ball valves, and air-locks, with the tank. This approach adds convenience and immediate usability. Bulk purchases also lead to significant savings per tank. For example, buying multiple tanks at once can reduce the per-unit price and sometimes include free shipping or extra accessories.
| Number of Tanks Purchased | Approximate Price per Tank (USD) | Typical Included Accessories |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | $2,000 | Thermometer, ball valve, air-lock |
| 3 | $1,850 | Above + possible free shipping |
| 5 | $1,700 | Above + extra accessories |
| 10 | $1,500 | Above + further discounts |
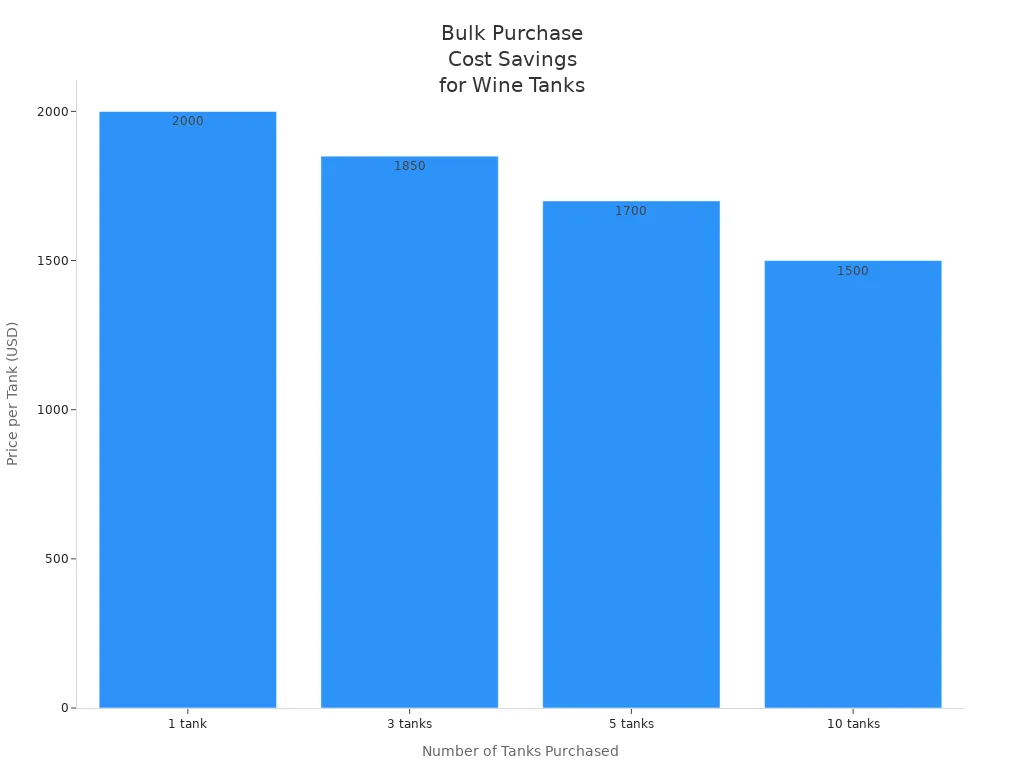
Note: Choosing tanks with bundled features and accessories can save money and streamline setup, especially for new wineries or those expanding production.
Brand Reputation and Seller Trustworthiness
Brand reputation and seller trustworthiness influence both the price and the long-term value of wine fermentation tanks. Buyers often pay a premium for established brands with a proven track record. These companies invest in research, quality control, and customer support. Their tanks usually meet strict industry standards and come with reliable warranties.
A reputable seller provides clear product specifications, transparent pricing, and responsive after-sales support. They help buyers understand the differences between tank models and guide them through the selection process. Trustworthy sellers also offer technical training, installation services, and ongoing maintenance support.
Shandong Chenma Machinery Co., Ltd. stands out as a trusted manufacturer in the industry. The company operates a large production facility with advanced machinery and a skilled engineering team. They adapt tanks to meet unique customer needs and offer both catalog and fully customized solutions. Their focus on quality, safety, and technical innovation ensures that buyers receive reliable equipment for their winemaking operations.
Tip: Always research the seller’s reputation before purchasing wine fermentation tanks for sale. Look for companies with a history of quality manufacturing, technical expertise, and strong customer support. This approach helps ensure a smooth buying experience and long-term satisfaction.
Key Features to Compare in Stainless Steel Wine Fermentation Tanks

Stainless Steel Grades: 304 vs. 316
Selecting the right stainless steel grade is essential when evaluating a stainless steel wine fermentation tank. The two most common grades, 304 and 316, differ in chemical composition and performance. The table below highlights their main differences:
| Element | 304 Stainless Steel | 316 Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Chromium (Cr) | 18-20% | 16-18% |
| Nickel (Ni) | 8-10.5% | 10-14% |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | None | 2-3% |
The presence of molybdenum in 316 stainless steel significantly enhances its resistance to corrosion, especially in environments with chlorides and organic acids. This makes 316 a preferred choice for wine fermentation, where acidic conditions and potential chloride exposure are common. While 304 stainless steel offers good corrosion resistance and is cost-effective, it is more vulnerable to pitting and crevice corrosion in harsh environments. Although 316 stainless steel costs about 20-30% more, its superior durability and longevity often justify the investment for wineries seeking long-term value.
Tip: For wine producers operating in environments with high acidity or chloride exposure, 316 stainless steel wine fermentation tanks provide better protection and longer service life.
Cooling Jackets and Temperature Control Options
Temperature control during fermentation plays a critical role in wine quality. Cooling jackets, which wrap around the tank, allow precise regulation of internal temperatures. The table below compares jacketed fermentation tanks with non-jacketed models:
| Feature/Aspect | Jacketed Tanks with Cooling Systems | Non-Jacketed Tanks |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control Precision | ±0.3°C | ±1.5°C |
| Energy Efficiency | Use about 30% less coolant | Higher coolant usage |
| Cleaning & Hygiene | CIP compatible, polished interiors | Less optimized for cleaning |
| Price Range (Commercial Scale) | $3,500 to over $10,000 | $1,500 to $2,100 |
| Advanced Features | AI monitoring, modular scalability | Typically not included |
Jacketed fermentation tanks enable winemakers to maintain stable temperatures, which prevents off-flavors and ensures consistent fermentation. These tanks also support clean-in-place (CIP) systems, reducing cleaning time and improving hygiene. Thermoregulated fermenters, equipped with advanced temperature control systems, further enhance precision and energy efficiency. Although the initial investment is higher, the benefits in product quality and operational savings make these tanks a popular choice for both small and large wineries.
Note: Investing in precise temperature control systems helps stabilize yeast activity, improves wine consistency, and reduces the risk of spoilage.
Automation, Control Systems, and Monitoring
Modern stainless steel wine fermentation tanks often feature automation and monitoring systems that streamline the winemaking process. These systems use sensors to track variables such as temperature, sugar content (Brix), and liquid levels. The table below outlines common automation and monitoring technologies:
| Automation/Monitoring System | Purpose | Technology/Method | Impact on Cost and Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Maintain ideal fermentation temperature | Cooling jackets, sensors, control units | Improves quality, reduces manual labor |
| Level Monitoring | Manage headspace, prevent overfills | Ultrasonic/capacitive sensors | Prevents spills, optimizes capacity |
| Brix Monitoring | Track sugar content for fermentation progress | Inline refractometers, densitometers | Enables informed decisions, improves consistency |
| SCADA Integration | Centralized monitoring and control | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition | Automates responses, enhances efficiency |
| Software/Data Analytics | Analyze trends, automate adjustments | Advanced software platforms | Supports data-driven decisions, scalability |
Automation reduces manual oversight, lowers labor costs, and minimizes the risk of spoilage or stuck fermentations. Real-time data from sensors allows winemakers to identify trends, troubleshoot issues, and make precise adjustments. Integrated management software connects operational data to financial records, improving inventory costing and profitability analysis. While the upfront investment in automation can be significant, the long-term savings and efficiency gains make these systems attractive for wineries aiming to scale production and maintain high quality.
Pro Tip: Automation and monitoring systems help wineries achieve consistent results, reduce waste, and support premium pricing through improved product quality.
Custom Fittings, Valves, and Modifications
Custom fittings, valves, and modifications play a crucial role in the performance and value of wine fermentation tanks. Wineries often request these enhancements to meet specific production needs or to improve workflow efficiency. Each customization can influence both the initial investment and the long-term usability of the tank.
- Tanks with internal coils, such as a 500-gallon model priced at $4,750, provide built-in temperature control. This feature eliminates the need for separate cooling equipment and helps maintain precise fermentation conditions.
- Mixing mechanisms, found in specialized tanks like a 500-gallon mixing tank at $12,646.50, ensure product uniformity. These systems reduce manual labor and improve consistency, which justifies the higher price.
- Custom dimensions and unique shapes help wineries maximize available space. These modifications make the tanks easier to fit into existing facilities but often increase manufacturing costs.
- Specialized finishes, such as polished interiors, enhance cleaning and hygiene. These finishes also improve corrosion resistance, which extends the tank’s lifespan.
- Additional ports and fittings, including sample valves and extra access points, expand the tank’s functionality. These features allow for easier sampling, cleaning, and integration with other equipment.
Popular customizations like extra ports, polished interiors, cooling jackets, and custom sizes help wineries adapt to changing production needs. These enhancements improve fermentation quality and can reduce operational costs over time.
| Winery Location | Customization Benefit | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| California | Added temperature control features | 20% increase in customer satisfaction ratings |
| New Zealand | Tanks designed to preserve acidity | Higher critic scores and increased sales |
Manufacturers such as Chenma offer a wide range of custom options. Their engineering teams work closely with clients to design tanks that match specific requirements. This approach ensures that each tank delivers optimal performance, hygiene, and efficiency for the winery’s unique process.
Certifications, Compliance, and Safety Standards
Certifications, compliance, and safety standards are essential factors when selecting wine fermentation tanks. These elements guarantee that the equipment meets industry regulations and supports safe, high-quality production.
- Certified tanks comply with international standards, such as ISO and CE. These certifications confirm that the tanks use food-grade materials and meet strict manufacturing guidelines.
- Compliance with local and global regulations ensures that the tanks are safe for use in food and beverage production. This reduces the risk of contamination and supports product quality.
- Safety features, including pressure relief valves and secure manways, protect workers during operation and maintenance.
- Tanks with documented traceability allow wineries to track materials and manufacturing processes. This transparency supports audits and quality assurance programs.
- Manufacturers like Chenma provide tanks with full documentation, including certificates of origin, material test reports, and compliance statements.
Note: Always verify that the wine fermentation tank includes all necessary certifications and safety features. This step protects both the winery’s investment and the quality of the final product.
Certifications and compliance not only ensure legal operation but also build trust with customers and regulatory agencies. Wineries that invest in certified equipment demonstrate a commitment to safety, quality, and industry best practices.
How to Compare Quotes for Wine Fermentation Tanks for Sale
Reviewing Detailed Product Specifications
When comparing quotes, buyers should carefully review the product specification sheet for each tank. A detailed specification sheet provides clear information about the tank’s construction and features. Important details include:
- Material type, such as SUS304 or SUS316L stainless steel, with certified material test reports.
- Customizable tank capacity and dimensions, ranging from 100L to 10,000L.
- Design pressure, usually between 0.2 and 0.4 MPa, with tanks pressure tested at three times the operating pressure.
- Tank shape, often a vertical circular body with a stainless steel dished top and a 60° conical bottom for efficient yeast discharge.
- Cooling system, such as a dimple jacket with double glycol inlets and two-stage cooling.
- Insulation, typically high-grade polyurethane with a thickness of 60-100mm.
- Surface finish, with inner surfaces polished to Ra0.4μm for hygiene.
- 100% TIG welding for sanitary joints.
- Fittings and accessories, including sanitary clamp connectors, pressure relief valves, gauges, thermometers, sampling valves, manholes, and a 360° CIP cleaning system.
- Adjustable stainless steel legs, lifting lugs, racking arm, and hops adding port.
- Compliance with standards like GB150-2011 and NB/T 47003.1-2009.
- Quality control measures, such as metal spectrum analysis and roughness detection.
A thorough review of these specifications helps buyers understand the value and suitability of each tank for their production needs.
Understanding Warranty and After-Sales Support
Warranty terms and after-sales support can differ greatly among manufacturers. Buyers should compare the length of warranty, coverage details, and available support services. The table below summarizes common warranty offerings:
| Manufacturer / Tank Type | Warranty Period | Coverage Focus | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Suppliers | 3 to 5 years | Materials and workmanship | Typical warranty range |
| Chenma | 3 years | Tank and core components | Free replacement parts during warranty |
| Various Suppliers | 5 years | Stainless steel durability | Standard for steel quality |
Manufacturers like Chenma also provide on-site installation, technical training, and lifelong technical advice. Comprehensive after-sales support reduces downtime and ensures smooth operation. Buyers should check for clear service agreements, response times, and the scope of technical assistance.
Evaluating Delivery, Installation, and Import/Export Costs
Delivery, installation, and import/export costs can significantly affect the total price of wine fermentation tanks for sale. Buyers should consider:
- Freight, insurance, port handling, and packaging costs, which may be higher for remote locations.
- Import tariffs, VAT/GST, and local compliance fees that impact the final landed price.
- The use of experienced freight forwarders and independent inspection agencies to reduce delivery risks.
- The importance of clarifying Incoterms (such as EXW, CIF, or DDP) to determine shipping and import responsibilities.
- Regional logistics challenges and certification requirements that may add to costs.
A comprehensive quote should include all these factors. Buyers who clarify trade terms and negotiate for a complete package, including after-sales support, can better manage their total cost of ownership.
Identifying Hidden Fees and Extra Charges
When purchasing wine fermentation tanks, buyers often focus on the base price. However, several hidden fees and extra charges can impact the total investment. Recognizing these costs early helps wineries avoid budget surprises and plan more effectively.
Many buyers overlook the need for permits and compliance fees. Alcohol production permits and related regulatory costs can add up quickly. These fees vary by region and may require annual renewals. Insurance for equipment and operations also increases expenses. Proper coverage protects against accidents, but it comes with ongoing premiums.
Renovation costs for vineyard infrastructure and cellar setups often surprise new buyers. Upgrading electrical systems, reinforcing floors, or improving ventilation may become necessary before installing new tanks. These improvements ensure safe and efficient operations but can strain budgets if not anticipated.
Maintenance and warranty costs represent another area of ongoing expense. While some manufacturers include basic warranties, extended coverage or service agreements may require additional payment. Regular maintenance keeps tanks in top condition but adds to yearly costs.
Investments in automation and advanced technology can also lead to extra charges. Features like remote monitoring, control systems, or custom fittings often carry separate fees. Buyers should confirm what is included in the initial quote and what counts as an upgrade.
Unplanned events, such as equipment breakdowns or crop failures, highlight the importance of contingency funds. Without a financial buffer, wineries may face unexpected strain during challenging seasons.
- Common hidden fees and extra charges include:
- Alcohol production permits and compliance fees
- Insurance premiums for equipment and operations
- Renovation and infrastructure upgrades
- Maintenance and extended warranty costs
- Additional charges for automation or custom features
- Contingency funds for emergencies
Tip: Always request a detailed quote that lists all potential fees. Careful planning and open communication with suppliers help prevent costly surprises and support long-term success.
Value vs. Cost When Buying Stainless Steel Wine Fermentation Tanks

Balancing Quality, Price, and Long-Term Value
Selecting the right wine fermentation tank involves more than just comparing prices. Buyers must weigh quality, initial investment, and the long-term benefits each material offers. The table below highlights how different tank materials compare in terms of quality, cost, and suitability for various winemaking needs:
| Material | Quality Impact & Flavor Effects | Price & Maintenance Considerations | Long-term Value & Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Excellent sealing prevents oxidation; maintains freshness and fruity aroma; easy to clean; corrosion-resistant. | Higher initial cost; low maintenance and cleaning costs. | Durable and suitable for long-term use; often equipped with temperature control systems for precise fermentation. |
| Oak | Oxygen permeable; softens tannins; adds complex wood aromas (vanilla, caramel); ideal for aging. | Expensive; requires regular replacement and higher maintenance costs. | Best for wineries focusing on high-quality, personalized wines; suitable for long-term aging. |
| Cement | Slightly permeable; balances wine structure; no wood flavor; good insulation for stable temperature. | Moderate price; low maintenance costs. | Long service life; suitable for stable production and traditional winemaking. |
| Ceramic | Good air permeability; supports micro-oxidation without affecting fruity aroma; fragile. | Expensive; fragile; high transportation and maintenance costs. | Suitable for small-scale, boutique, or organic wine production; less ideal for large-scale use. |
A high-quality stainless wine tank stands out for its durability, ease of cleaning, and ability to maintain wine freshness. Although the upfront cost is higher, the long-term value often outweighs the initial investment.
Assessing Durability, Maintenance, and Lifespan
Durability and maintenance play a major role in the total cost of ownership. Several factors contribute to the long lifespan of a high-quality stainless wine tank:
- Thicker stainless steel construction increases durability.
- Airtight environments prevent oxidation and preserve tank integrity.
- Smooth, non-porous surfaces reduce bacterial growth and simplify cleaning.
- Corrosion resistance protects against acidic grape juice.
- Integration of cooling jackets and CIP systems supports longevity.
- Lower maintenance needs and costs compared to oak barrels.
Routine preventive maintenance, such as regular inspections and cleaning, extends equipment life and reduces unexpected repair costs. Using quality parts and training staff for minor repairs also helps control expenses over time.
Considering Resale Value and Upgradability
Resale value and upgradability add to the overall value of a stainless steel tank. Tanks made from high-grade materials retain their worth longer and attract buyers in the secondary market. Features like modular fittings, temperature control systems, and customizable ports make it easier to upgrade or adapt tanks as production needs change. Wineries that invest in adaptable equipment can scale operations efficiently and recover more value if they decide to sell or trade their tanks in the future.
Practical Tips and Buyer Checklist for Wine Fermentation Tanks for Sale
Researching Seller Reputation, Including SDCHENMA
Buyers should always investigate the reputation of wine fermentation tank suppliers before making a purchase. Comparing different sellers helps identify those with strong market presence, technical expertise, and reliable after-sales support. The table below highlights how buyers can compare suppliers based on specialties and reputation:
| Supplier Name | Specialties | Reasons to Choose | Market Presence / Reputation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pretank | Open-top, closed tanks, pump-over fermenters | Competitive pricing, custom fittings | Strong in Asia, export-ready |
| Gortani Srl | Thermoregulated fermenters, vinificators | Precise temperature control, automation | Used by top Italian wineries |
| Letina | Open/closed tanks, floating lids | Flexible for small-medium wineries | Strong in North America, Europe |
| Speidel | Jacketed, conical, flat-bottom tanks | German engineering, durable design | Well-known German reputation |
SDCHENMA, also known as Shandong Chenma Machinery Co., Ltd., specializes in stainless steel fermentation equipment and custom solutions. Buyers can research SDCHENMA by reviewing their technical capabilities, production scale, and history of turnkey projects. Direct contact with the company and requests for case studies or technical documentation further support informed decisions.
Requesting Detailed Quotes and Product Comparisons
A detailed quote allows buyers to compare tank options and understand what each supplier offers. Key elements to request in a quote include:
- Tank material (stainless steel, wood, plastic, glass) and grade
- Size and capacity matched to production needs
- Temperature control systems, such as cooling jackets
- Stirring and pumping systems for fermentation efficiency
- Tank design type (flat-bottom, jacketed, conical, variable capacity, pressure)
- Cleaning and maintenance requirements
- Budget breakdown: initial cost, maintenance, and long-term value
- Supplier reputation and after-sales service
- Accessories included (sample valves, stands, airlocks)
- Customization options and impact on wine quality
| Tank Type | Description | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Flat-Bottom Tanks | Basic, vertical design | Versatile fermentation styles |
| Jacketed Tanks | Double wall for temperature control | Red wine needing precise temperature |
| Conical Bottom Tanks | Cone-shaped for sediment removal | Red wine, color and tannin extraction |
| Variable Capacity Tanks | Floating lid adjusts volume, reduces oxidation | Small-batch or variable volume production |
| Pressure Tanks | Withstands higher pressures | Sparkling wine production |
Tip: Always ask for a side-by-side comparison of features, costs, and included accessories to make an informed choice.
Verifying Certifications and Safety Standards
Verifying certifications and safety standards ensures the tank meets industry requirements and supports safe winemaking. Buyers should follow these steps:
- Confirm welding seam integrity through Penetrant Testing (PT) and Radiographic Testing (RT) for compliance with standards like ASME.
- Check that the inner surface smoothness meets mirror-level standards (Ra ≤ 0.8 μm) to prevent bacterial growth.
- Ensure all consumables in contact with wine have food safety certifications (FDA/EC1935) and full material traceability.
- Request documentation of Factory Acceptance Tests (FAT), including pressure and hygiene tests.
- Obtain a quality assurance certificate with the manufacturer’s laboratory seal.
- Ask for an electronic ID or traceability record for each tank, tracking its manufacturing process.
Note: Proper certification and traceability protect both the winery’s investment and product quality.
Asking About Customization and Expansion Options
Wineries often seek tanks that match their unique production needs. Customization options help them achieve better control and efficiency during fermentation. Many manufacturers, including Chenma, offer a wide range of custom features for wine fermentation tanks.
- Temperature control systems, such as cooling jackets and temperature probes, help maintain stable fermentation conditions. These systems allow winemakers to adjust temperatures for different wine styles.
- Cap management systems support red wine fermentation by managing skin contact and color extraction. This feature improves the quality and consistency of red wines.
- Adjustable lids and wide openings make cleaning easier and improve fermentation efficiency. These features also help with adding ingredients or removing solids.
- Specialized tank designs, including cylindrical, conical, and unitanks, fit different winemaking processes. Each design offers specific benefits for various wine types.
Expansion options also play a key role as wineries grow. Scalable tank designs allow producers to increase capacity without major changes to their facility. Variable capacity tanks handle different batch sizes, giving flexibility as production scales up or down. Floating lids reduce oxidation and make it easy to top off tanks between batches.
Tip: Wineries should plan for future growth by leaving space for additional tanks and choosing materials that match their wine style and operational needs. Working with reputable manufacturers who offer custom solutions and technical support ensures long-term success.
Planning for Future Needs and Scalability
Planning for future growth helps wineries avoid costly changes later. Several important factors guide this process:
1. Select a site with enough space for expansion and easy transportation access. 2. Design a flexible layout that supports adding new tanks or equipment without disrupting current operations. 3. Plan utility systems, such as water, electricity, and drainage, to meet both current and future needs. 4. Use high-quality materials and install drainage systems that can handle increased production. 5. Allocate space for tanks, bottling lines, and other equipment with scalability in mind. 6. Design cellar and barrel rooms with adjustable racking and proper temperature and humidity control. 7. Invest in modular and scalable equipment for fermentation, filtration, and bottling. 8. Implement winery management software that can grow with the business. 9. Ensure compliance with all regulations and plan for possible changes. 10. Incorporate sustainability practices, such as energy efficiency and water conservation.
A well-planned facility uses modular tank layouts and standardized piping to make expansion easier. Maximizing vertical space with multi-level platforms saves floor space and improves workflow. Consulting with experts, such as architects and winemaking consultants, helps optimize the design for both current and future needs. Phased implementation allows wineries to grow in stages, matching expansion to demand and available resources.
Selecting the right wine fermentation tank requires careful attention to both quality and value. Buyers should:
- Review tank specifications and included features.
- Compare seller reputations, such as SDCHENMA, for reliability.
- Request detailed quotes to understand total costs.
Taking time to compare options helps buyers invest in a tank that fits their needs and budget.
FAQ
What is the typical lifespan of a stainless steel wine fermentation tank?
A high-quality stainless steel tank often lasts 20 years or more. Proper cleaning and regular maintenance extend its service life. Many wineries use these tanks for decades without major issues.
How do cooling jackets improve wine fermentation?
Cooling jackets help control the temperature inside the tank. This control allows winemakers to manage yeast activity and prevent spoilage. Consistent temperatures lead to better wine quality.
Can wineries customize tank features to fit unique needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer custom options. Wineries can request specific fittings, sizes, or automation features. Customization helps match the tank to production goals and facility layouts.
What certifications should buyers look for in wine fermentation tanks?
Buyers should check for food-grade certifications like ISO or CE. These certifications ensure the tank meets safety and hygiene standards. Documentation supports compliance with industry regulations.
Are there hidden costs when purchasing wine fermentation tanks?
Some costs may not appear in the initial quote. These can include shipping, installation, permits, and maintenance. Buyers should request a detailed breakdown to avoid surprises.



